Crown and Bridge
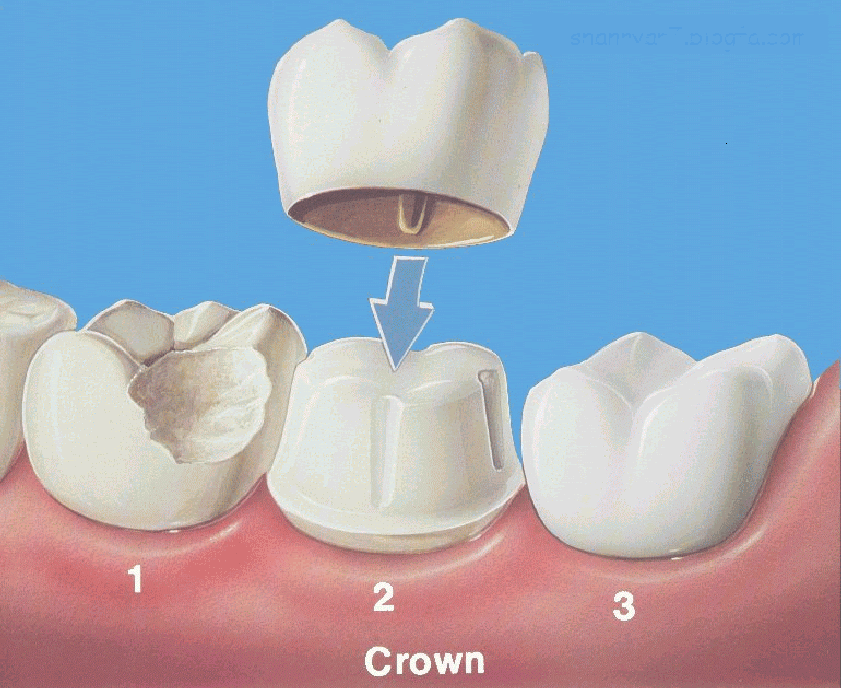
Crown
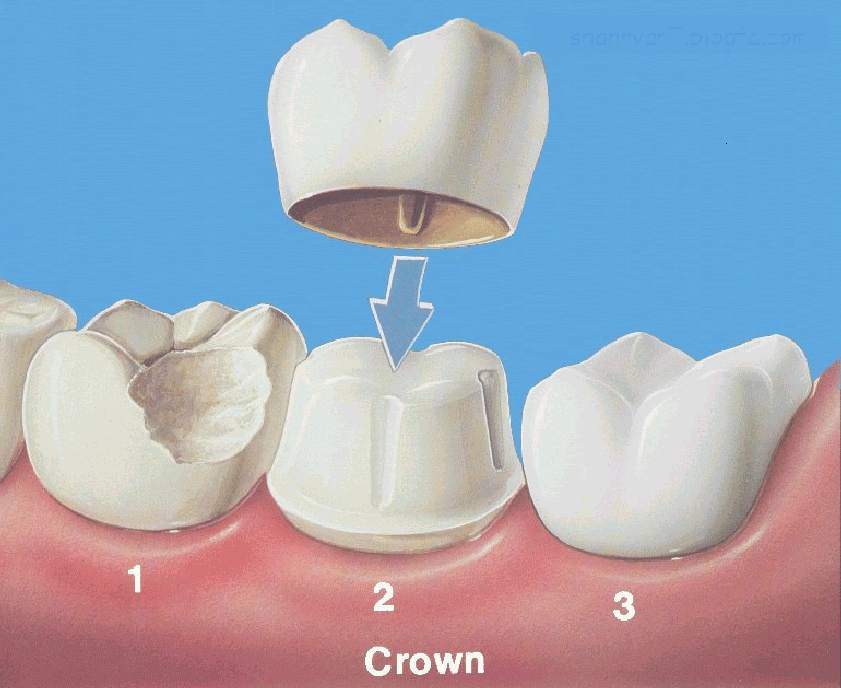
Crowns are full coverage restorations that are used to cover a tooth that is likely to break, or is too broken down to be restored with a filling. They are most commonly done after root canal treatment, or when a large filling wears out. The larger the hole made by a cavity that has to be treated, the more likely a crown will be needed. Even after a filling is put in a large cavity, a tooth is more likely to break. Keep in mind that the jaw muscles are the strongest in the human body. Teeth are subjected to tremendous pressures. Crowns ride over the weakened tooth, providing strength and protecting the tooth against breakage. A broken or cracked tooth is a far more serious matter and much more difficult to treat. Crowns prevent this, as well as making for a nice smile. It takes two appointments to restore a tooth with a crown. In the first any decay is removed from the tooth and it is shaped to accept the crown. Then an impression is made of the tooth for use in fabricating a crown. Between the two visits the crown is made, usually of high-strength porcelain over gold alloy, all ceramic material, or gold. During this time a temporary
crown is worn. In the second visit this temporary is removed. Then the permanent crown is adjusted as needed and then cemented in place.
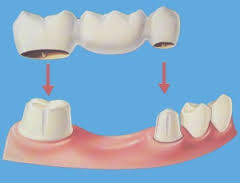
 Bridge
Bridge
This is an option for filling the space created by a missing tooth. It is formed to look like the missing tooth, and it takes its place in the mouth. The sides of a bridge use the two surrounding teeth for support, hence the name. A bridge replaces the missing tooth, both functionally and cosmetically. Bridge work is as much an art as it is an exact science. The materials used may be gold alloys, porcelain bonded to metal alloy, or all ceramic material. The choice of material depends on requirements for strength, wear, and/or esthetics. It is important that a missing tooth be replaced as soon as possible for several reasons. If not treated the teeth surrounding the gap begin to shift inward, creating a whole chain reaction of bad things. Teeth use their neighbors for support, and, with one missing, they start to "fall." As this worsens the bite changes in response to the pressure. This can eventually result in problems with the entire jaw, e.g. TMJ. The surrounding teeth deteriorate and it is just a matter of time before they, too, are lost. Gum disease becomes a serious problem, with the difficulty of treatment increasing as the neglect continues.
crown is worn. In the second visit this temporary is removed. Then the permanent crown is adjusted as needed and then cemented in place.
 Bridge
BridgeThis is an option for filling the space created by a missing tooth. It is formed to look like the missing tooth, and it takes its place in the mouth. The sides of a bridge use the two surrounding teeth for support, hence the name. A bridge replaces the missing tooth, both functionally and cosmetically. Bridge work is as much an art as it is an exact science. The materials used may be gold alloys, porcelain bonded to metal alloy, or all ceramic material. The choice of material depends on requirements for strength, wear, and/or esthetics. It is important that a missing tooth be replaced as soon as possible for several reasons. If not treated the teeth surrounding the gap begin to shift inward, creating a whole chain reaction of bad things. Teeth use their neighbors for support, and, with one missing, they start to "fall." As this worsens the bite changes in response to the pressure. This can eventually result in problems with the entire jaw, e.g. TMJ. The surrounding teeth deteriorate and it is just a matter of time before they, too, are lost. Gum disease becomes a serious problem, with the difficulty of treatment increasing as the neglect continues.



